Zing Ring
"Supporting Remote Communication with Hand Interactions"
Overview
“Supporting Remote Communication with Hand Interactions”
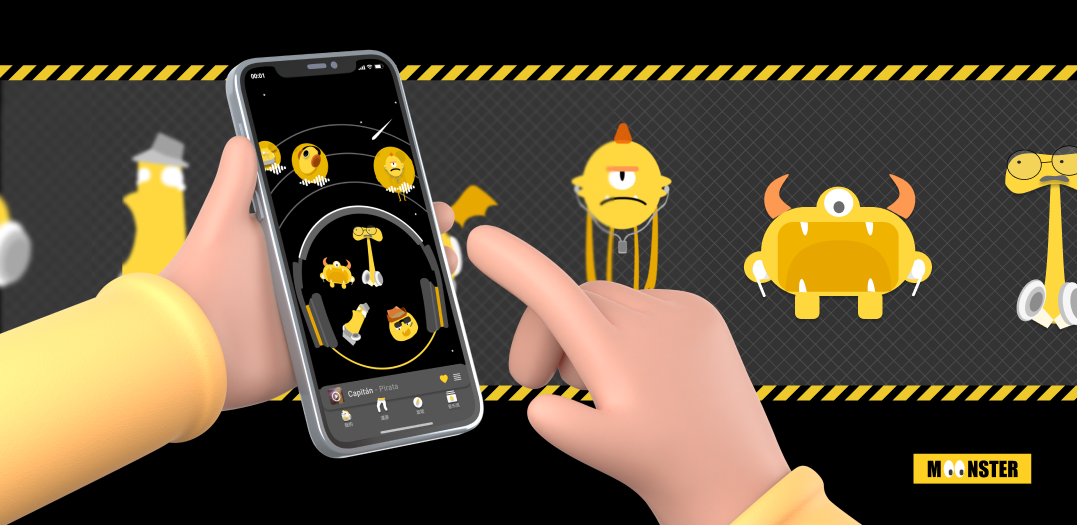
Zing Ring is a wearable platform that allows personalized, continuous and tangible support for remote communication. It utilizes hand gestures as a supplementary of intense communication.
This project is an application of Dual IMU Rings developed by PI Lab, inspired by the difficulties encountered by people in remote relationships during the COVID-19.
Role
Solo Project (Based on existing research)
Duration
2023 Nov. – 2023 Dec. (2 months)
Collaborator
Chen Liang, Pervasive HCI Lab, Tsinghua
Category
Wearable, IMU, Remote Communication
Platform
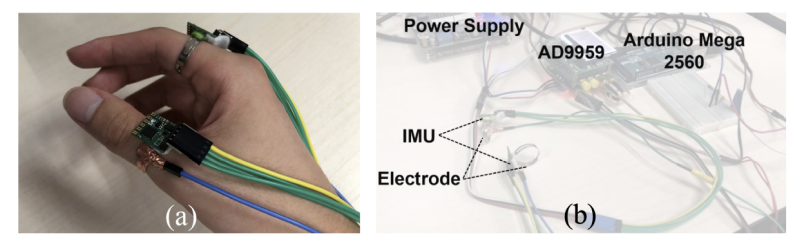
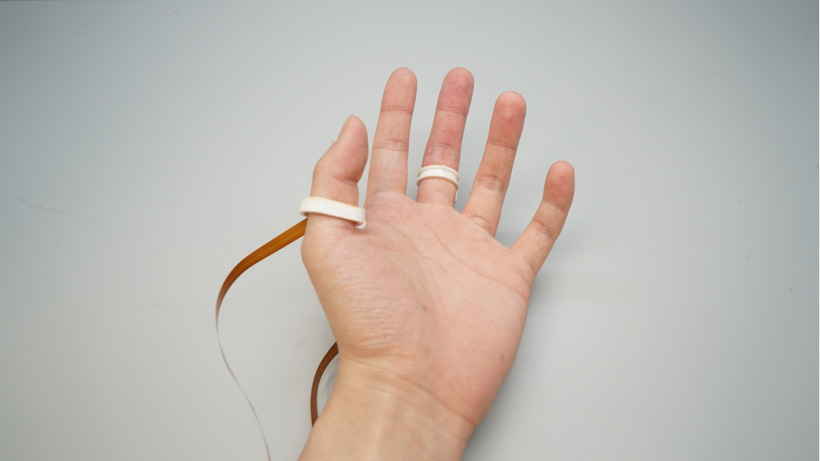
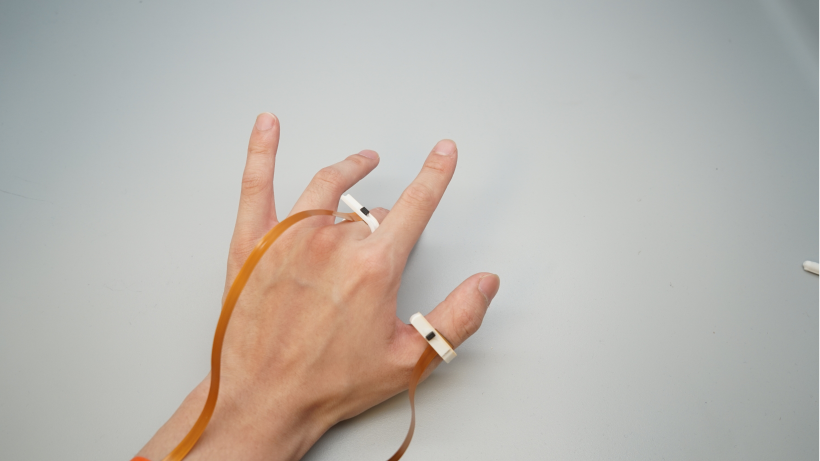
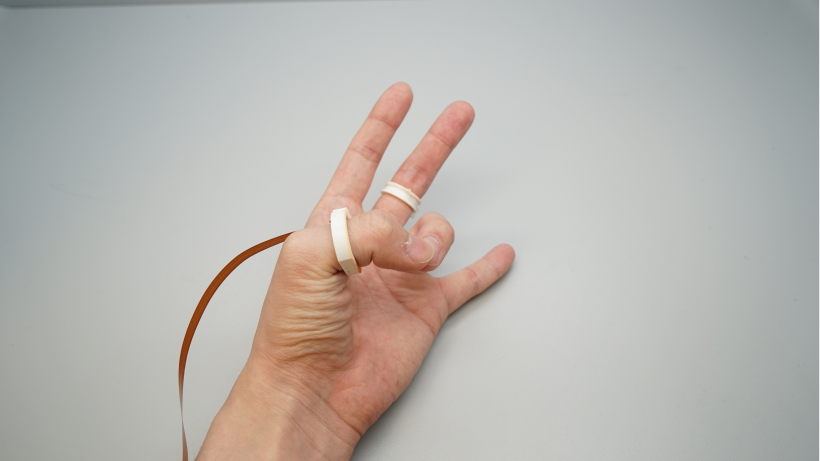
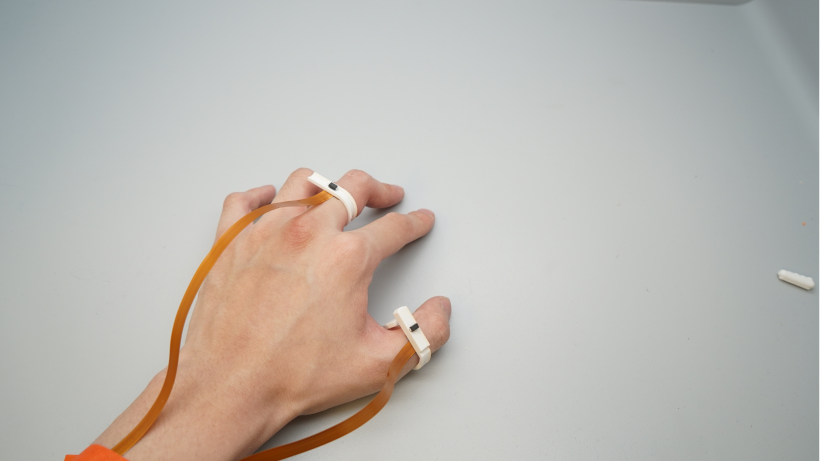
I was introduced to DualRing during my undergraduate research at Pervasive HCI Lab. This is a novel dual-ring input device that captures the state and motion of the user’s hand and fingers. The DualRing’s two IMU rings are fixed to the user’s thumb and index finger, and can sense not only absolute gestures relative to the ground, but also relative postures and movements between hands.
Absolute gestures relative to the ground are sensed, as well as relative postures and movements between the hands. In order to realize natural thumb-finger interaction, as well as a high-frequency AC circuit for body contact detection was developed. Based on the sensing information, the interaction space was de-emphasized and divided into three subspaces: intra-hand interaction, hand-surface interaction and hand-object interaction.
Design Space
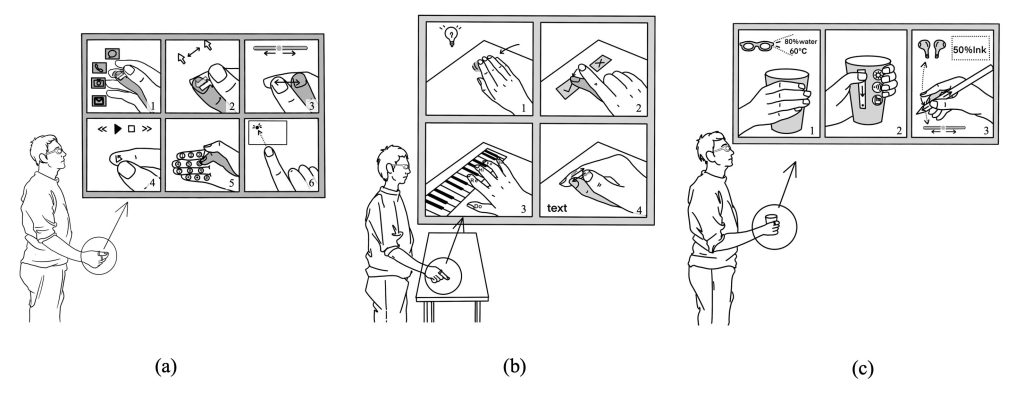
a. Within-hand Interaction
Since DualRing provides accurate orientation data of both the thumb and the index finger, it can support various types of primitive thumb-to-finger operants, including pinching, continuous cursor control, region selection, sliding, and pattern drawing.
b. Hand-to-surface Interaction
DualRing can sense the state and the movement of both the touching finger and the non-touching fingers. Therefore, it has the potential to detect the state of the whole hand and support a wider range of gesture set.
c. Hand-to-object Interaction
Another important subspace enabled by DualRing is to interact with different objects in real-life scenarios. The gripping events and the gestures on the surface can be sensed, allowing the user to interact with ordinary objects, such as a bottle, a box, or a ball.
Investigation
Interview :
on difficulties in remote relationships
Steve Wan & Cici (Phd Students)
The lack of a sense of presence in long-distance relationships frequently results in feelings of loss. This arises from various elements, predominantly the absence of physical touch.
Grace Lee & Jacky Tang (Architect & Designer)
Remote relationships often face greater challenges. Minor conflicts are not easily mended, primarily because of the lack of communication opportunities.
FF & GG (Phd Students)
We find it difficult to establish empathy in remote communication, as we lack the richness of facial expressions and body language.
Insights
Lack of physical touch leads to the sense of absence.
Lack of minor communication opportunity hinders solving of minor conflicts.
There’s a gap of media (carrying more emotional info) in remote communication.
Integrated Solution

Combining rings with emotion transmission technology allows couples to convey emotions through the rings, enabling the expression of longing even when they are physically apart.

Making gesture interactions for emotional expression less deliberate aims to render emotional communication more natural.

Utilizing existing hardware interfaces to facilitate recording and communication while establishing a “Love Line” ensures a more direct and secure avenue for privacy.
Prototype
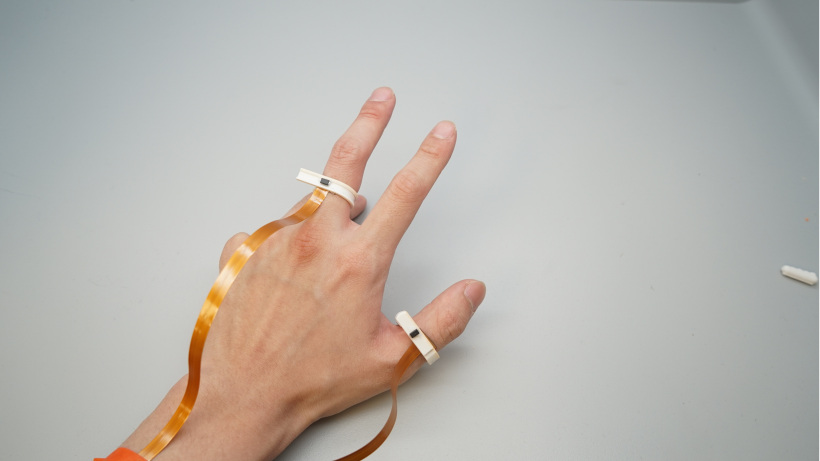
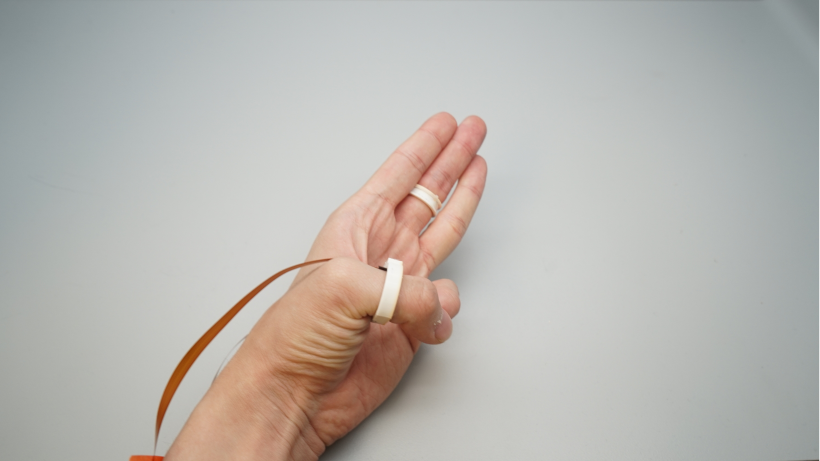
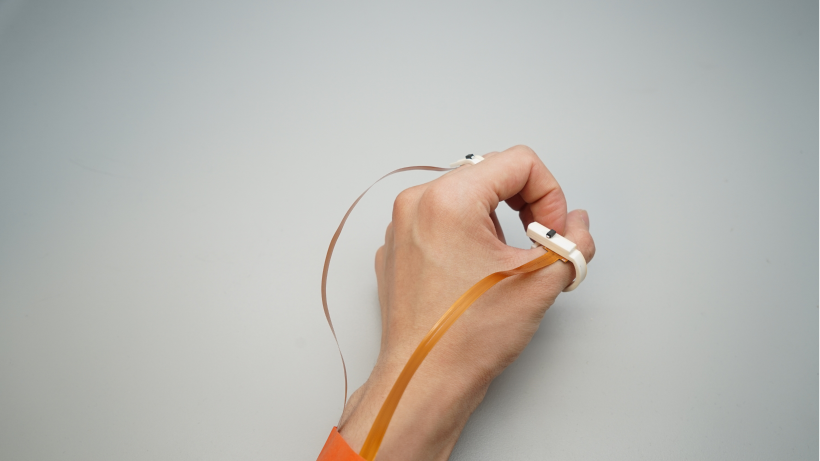




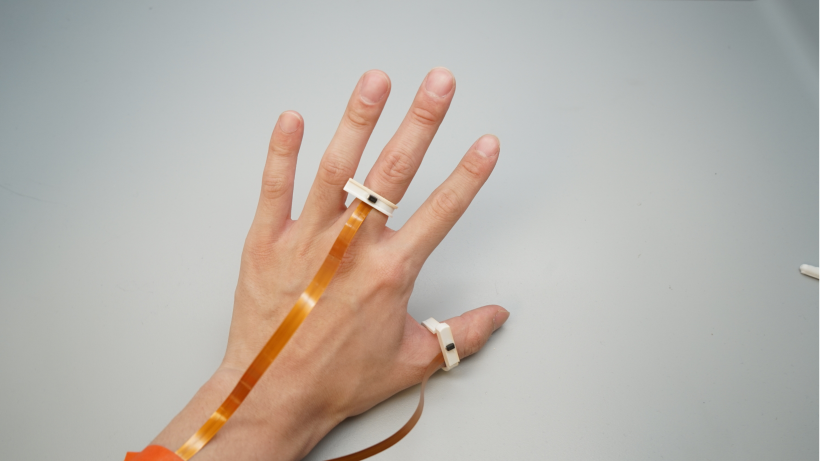






Experiments
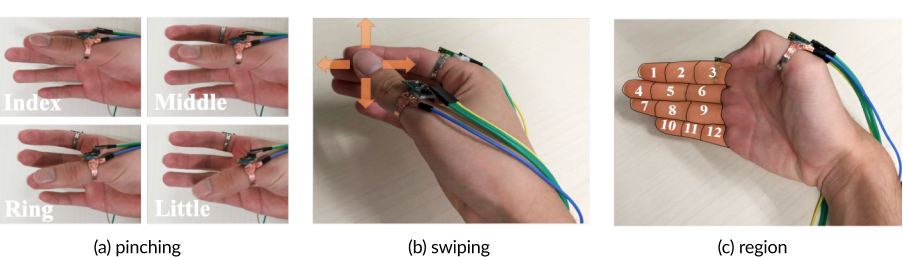
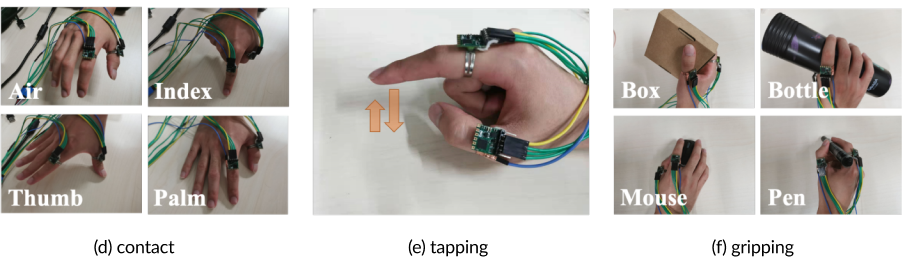
The gesture sets for system evaluation. (a) Pinching gestures; (b) Swiping gestures; (c) Touching different finger segments; (d) Contact gestures; (e) Tapping gestures; (f ) Gripping gestures.
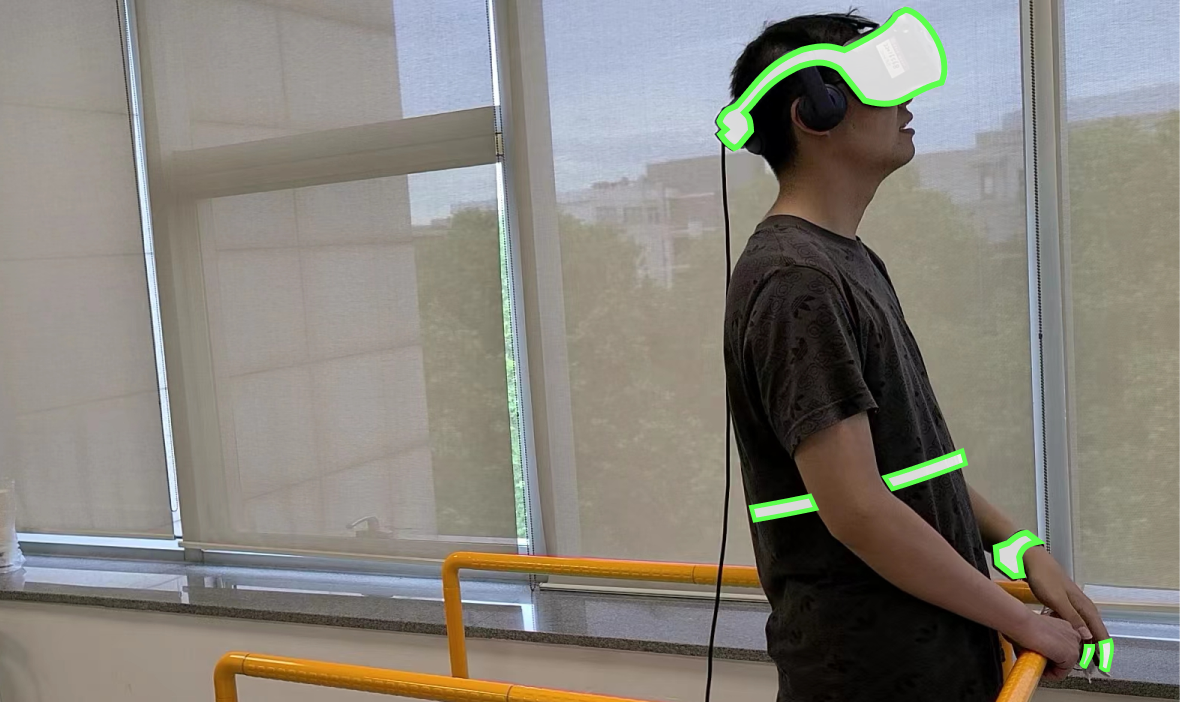
User Tests
Interactive programs for the user study. we conducted a user study to understand users’ subjective preference and comments on differenthand gestures in our design space.

Left: Real-time visual feedback demos for:
1) signal amplitude of pinching and 2) probability distribution of contact gestures, tapping gestures, and gripping gestures.
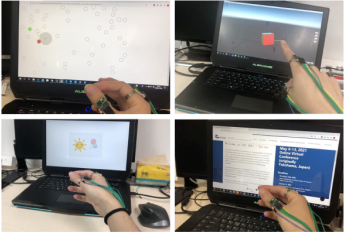
Right: Demonstrative applications for 1) finger cursor, 2) ray pointing, 3) finger pattern, and 4) finger sliding
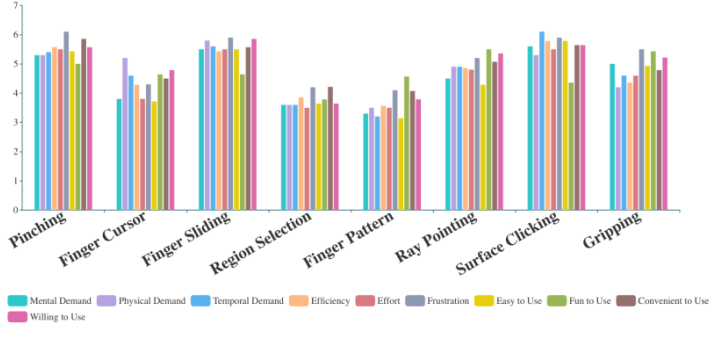
The figure above shows the subjective ratings of different gestures in the ten dimensions. Higher score indicates lower
mental demand, lower physical demand, lower temporal demand, higher efficiency, lower effort, lower frustration,
easier to use, more fun to use, more convenient to use, and more willing to use.
Subjective ratings of different gestures in different aspects. Higher score indicates lower mental demand, lower physical demand, lower temporal demand, higher efficiency, lower effort, lower frustration, easier to use, more fun to use, more convenient to use, and more willing to use.